InSb MQW - AFM Topology
A common attribute of the InSb quantum well material is a surface with a high density
of "hillocks". The structures average a height of 15 nm with contour angles of 0.35°.
The second attribute of the material is a tendancy for the hillocks to be elongated in
the [1 -1 0] direction. This is attributed to the anitrosopy of the diffusion length.
The third and most intriguing surface feature are the 'Oriented Abrupt Steps' (OAS).
Just as the elongation, the OASs are predominantly oriented in the [1 -1 0] direction.
The steps have an agressive angle of ~10 degrees.
S498
25 x [25 nm InSb 50 nm 9% AlInSb]
(click on image to enlarge)
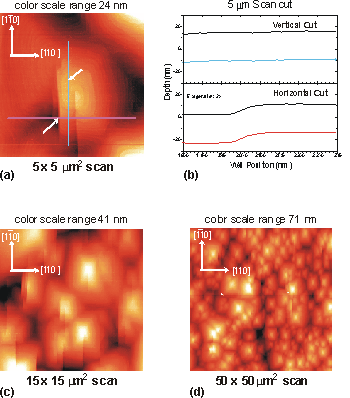
The three figures: (a), (c) and (d) are AFM images of the same sample at different latteral resolutions.
Figure (a) is 5 mm2 scan showing a detailed image of a hillock.
The graduating color rings about the hillock are steps of one atomic layer (~10 Å) which form the basis of a
screw dislocation. The red and blue lines as well as the arrows in the figure indicate the location of cross-sectional
plot in figure (b). A simulated well profile is also shown with the horizontal axis exagerated by a factor of 2
to clarify the compression of the well thickness due to the step in the hillock.
Using the 15 and 50mm2 scans (figures (c) and (d) respectively) the
hillock and O.A.S. density and size were
calculated for comparison to the optical
and crystalline properties of the
sample.
|
|




